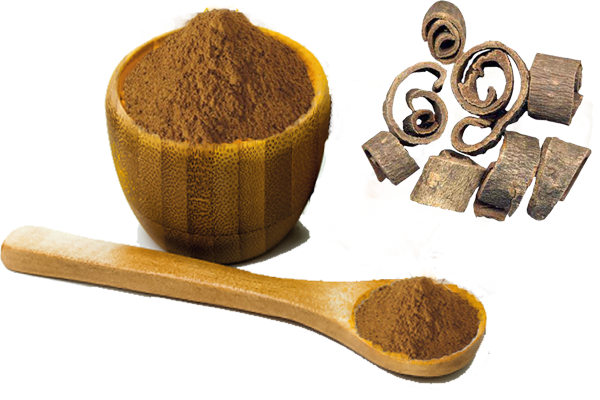
Magnolia Bark Extract Powder
Magnolia Bark Extract Powder
Magnolia Bark Extract Powder 2% ~98% by HPLC with analysis meets the EP, USP, JP, CP....
Magnolia Bark Extract Powder
Latin Name: Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis
Extracting Part: Bark
Supplied Purity: Magnolol 2% ~98% by HPLC,
Honokiol 2%~98% by HPLC,
Magnolol + Honokiol 5%~98% by HPLC
Quantity Provided: 1kg, 5kg, 10kg, 100kg, 1000kg per month
Application & Functional:
Cosmetics: Natural antiseptic, anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, anti-aging, acne removal and other multiple skin care effects.
Oral Care: To prevent dental caries, gingivitis, periodontitis and halitosis
Health Care: Protect liver, anti-depression, improve sleep, protect cardiovascular and cerebrovascular
Feed supplement: Healthy stomach, improve animal appetite

Magnolia Bark Extract Powder
Magnolia Bark Extract Powder Original
Traditional Chinese herbal drugs have been used for thousands of years in Chinese pharmacopoeia. The bark of Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E. Wilson, known under the pinyin name “Houpo”, has been traditionally used in Chinese and Japanese medicines for the treatment of anxiety, asthma, depression, gastrointestinal disorders, headache, and more. Moreover, Magnolia bark extract is a major constituent of currently marketed dietary supplements and cosmetic products. Much pharmacological activity has been reported for this herb and its major compounds, notably antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic and antispasmodic effects. However, the mechanisms underlying this have not been elucidated and only a very few clinical trials have been published. In vitro and in vivo toxicity studies have also been published and indicate some intriguing features. The present review aims to summarize the literature on M. officinalis bark composition, utilisation, pharmacology, and safety.
Magnolia trees are mainly distributed in East and Southeast Asia (Cui et al., 2013) and are generally very attractive thanks to their fragrant and dazzling flowers (Lee et al., 2011). The root and branch bark are collected from April to June and dried in the shade; the stem bark is slightly decocted in boiling water and piled up in a wet place until its inner surface becomes purplish-brown or dark brown, softened by steaming, and rolled and dried (CPC, 2010). The dried bark is gray-brown in color with oval lenticles in a longitudinal striation (Fig. (Fig.1)1) and has a fragrant odor, a pungent taste, and is slightly bitter (EPCNF, 2009).
Magnolia bark has been used as a constituent of various traditional Chinese formulas such as “Banxia Houpo Tang” (Table (Table1),1), “Xiao Zhengai Tang”, “Ping Wei San”, and “Shenmi Tang”. In China, a number of prescriptions containing Houpo are still in use in modern clinical practice (Yu et al., 2012). In Japan, two prescriptions containing Magnolia bark, Hange-Koboku-To (Japanese name for Banxia Houpo Tang) (Iwasaki et al., 2000) and Saiboku-To (Table (Table1),1), are also still in use in modern clinical practice (Li N. et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2011).
Phytochemicals Isolated From Magnolia
Up till now, more than 250 kinds of ingredients have been isolated from the cones, bark, flowers, and leaves of the genus Magnolia (Cui et al., 2013). Chemical investigations of the cortex of M. officinalis and M. obovata led to the isolation of several major phenolic compounds, notably the neolignan derivatives magnolol (5,5′-diallyl-2,2′-dihydroxybiphenyl) and honokiol (5,3′-diallyl-2,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl) (Table (Table2),2), which are considered the two principal phenolic compounds in the bark and the main active constituents (Dharmananda, 2002; Li N. et al., 2007; EPCNF, 2009).
As well as these well-known lignans magnolol and honokiol, alkaloids are a group of interesting secondary metabolites of this species, which produces mainly isoquinoline-type alkaloids, the majority of which are aporphine and benzylisoquinoline derivatives (Yan et al., 2013). Magnolia bark also contains volatile oils, the major constituents of which are the sesquiterpenoid alcohols, α-, β-, and γ-eudesmol (about 95% of the essential oil). Specific components in the bark and the proportions of those constituents significantly differ depending on harvesting sites and period (EPCNF, 2009).
Biological Activity
Magnolia bark has not only been used historically in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine, but also in American and Indian medicine; the bark has been listed in the American Pharmacopeia as bitter tonic and antimalarial (Davis, 1981; Li N. et al., 2007). More recently, Magnolia bark has been used as a component of dietary supplements and topically applied cosmetics (Li N. et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2007).
Various pharmacological activities (anti-cancer, anti-stress, anti-anxiety, antidepressant, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective) have been investigated for Magnolia bark and its constituents. However, most often the mechanisms underlying these pharmacological effects have not been elucidated (Lee et al., 2011) below:
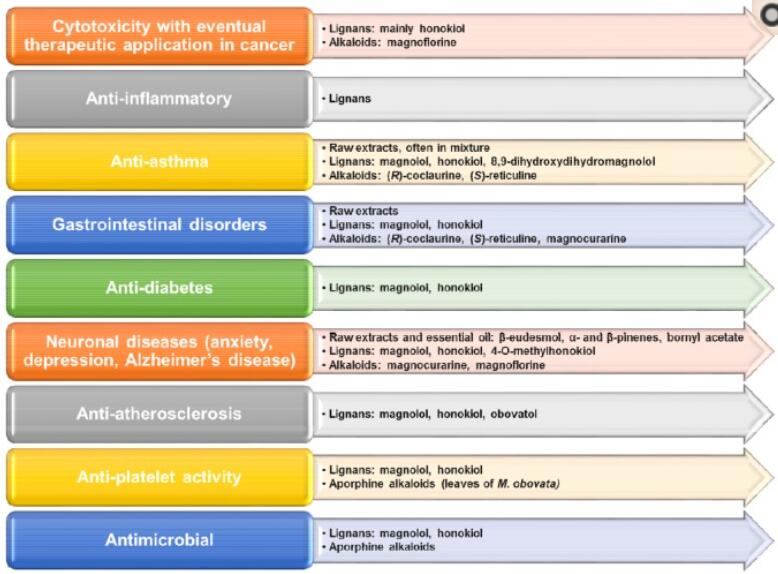
Magnolia Bark Extract Powder Therapeutic.jpg
Therapeutic application for Magnolia Bark Extract Powder
Effects on the nervous system
Recent studies have shown that Magnolia officinalis has significant effects on the nervous system, including antiepileptic, antidepressant, antidepressant, anti dementia, anti cerebral ischemia, and its main active component and magnolol are easy to pass through the blood-brain barrier, which has the potential to develop into a broad-spectrum anti nervous system disease drug
1. Antiepileptics
Magnolol can effectively inhibit the seizure of pentylenetetrazol induced epileptic rats. The EEG record shows that magnolol can prolong the latency of seizure, reduce the number of seizure peak and reduce the seizure grade. Its antiepileptic effect can be reversed by GABAA / flumazenil receptor antagonist. Chen et al. Also found that magnolol could reduce spontaneous epileptiform discharges and significantly reduce seizure induced Fos immunoreactivity in piriform cortex, gyrus cogwheel and hippocampal CAI.
2 Antidepressant
Magnolol can promote the regeneration of hippocampal neurons in depression mice induced by mild stimulation, increase the number of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and deoxyuridine positive cells in the hippocampus of mice, significantly increase the weight of mice, increase the level of spontaneous activity of mice, increase the times of crossing the grid, improve the basic sugar preference of mice, and shorten the immobility time of tail suspension and forced swimming The antidepressant effect of Shengli capsule. However, honokiol can increase the content of 5-HT and decrease the expression of indole 2,3-dioxygenase mRNA in the brain of mice with acute and chronic stress, so as to achieve the antidepressant effect.
3. Anti dementia
Lee et al. Found that intragastric administration of Magnolia officinalis extract containing 0.05% ethanol for 3 months could improve memory dysfunction and prevent the accumulation of protein A in the brain, and reduce the expression of B-site amyloid precursor protein lyase I (BACE1), amyloid precursor protein and its product C99 in Tg2576 mice. Yong et al. Found that ethanol Magnolia officinalis extract and 4-o-methyl and honokiol can prevent scopolamine (1 mg / kg) induced memory impairment in mice in a dose-dependent manner, inhibit the increase of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in cortex and hippocampus of mice, and inhibit AChE activity in vitro, which can be used for the prevention and treatment of AD It can significantly increase the contents of dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in the brain tissue of vascular dementia rats, reduce the damage of neurovascular unit caused by cerebral ischemia, inhibit the dark reaction of oxidative stress, enhance the antioxidant defense mechanism in the brain tissue, and thus significantly improve their learning, memory and behavior ability.
4. Anti cerebral ischemia
Liu et al. Found that oral administration of magnolol and magnolol can significantly reduce the neurobehavioral score of cerebellar ischemia-reperfusion injury (I-R) rats and spontaneously hypertensive stroke prone rats, reduce the water content in brain tissue of the former, and significantly increase the survival rate of the latter. Yu et al. Found that intravenous injection and magnolol can increase cerebral blood flow after global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, and may have anti-oxidation, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, inhibition of neutrophil infiltration and anti-inflammatory effects, which is related to the treatment of stroke.

Magnolia Bark Extract Powder . png
Effects on cardiovascular system
1.1 Hypotensive
After intragastric administration of magnolol for 3 W, the increase of blood pressure in young spontaneous gerbil rats was slowed down. Li Na found that honokiol can activate the sirt3-klf15 signaling pathway, reduce the levels of serum creatinine, urinary creatinine, urinary albumin and urea nitrogen in mice. In addition to reducing hypertension, honokiol can significantly improve renal function and reduce hypertensive renal damage.
1.2 To improve cardiac function,
Yiquan et al. Found that honokiol could improve cardiac function and antagonize early arrhythmia of reperfusion by reducing intracellular free calcium and calcium overload in myocardial cells of acute myocardial I-R rats. Xiao Jinshan et al. Reported that magnolol can significantly prolong the exhausting time of exhaustive exercise mice, reduce the cardiac weight index, reduce the transverse diameter of myocardial cells, reduce the contents of tumor necrosis factor-A (TNF-a) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) in myocardial tissue, and may up regulate peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) and down regulate the expression of IL-1 NF-kB expression can improve the myocardial hypertrophy induced by exhaustive exercise in mice.
Effect on digestive system
In the study of anti diarrhea Zhu Zi Ping, it was found that the alcohol extract of Magnolia officinalis had obvious anti diarrhea effect on mice with diarrhea caused by senna leaf. Magnolol and honokiol had obvious inhibitory effect on small intestinal charcoal propulsion and diarrhea caused by senna leaf in mice with diarrhea treated by rhubarb, and the effect of honokiol was better than that of honokiol. Further studies showed that magnolol and honokiol could inhibit the calcium transport process of epithelial cells by controlling the opening and closing of calcium activated potassium channels, gene expression and affecting the controlled calcium channels, so as to achieve the effect of anti diarrhea.
Improve gastrointestinal motility
Cheng et al. Found that both Magnolia officinalis and jianghoupu ethyl acetate extract could enhance gastrointestinal motility, promote intestinal propulsion rate, reduce ulcer rate and increase serum gastrin content in mice induced by hydrochloric acid. Miao et al. Found that magnolol can increase the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduce the level of malondialdehyde, significantly reduce the level of nitric oxide in small intestine, antagonize oxidative stress and regulate Cajal cells to improve gastrointestinal motility disorder caused by sepsis.
Liver protection
Liu et al. Found that after subcutaneous injection of high dose (20.0 mg / kg) and magnolol, the degree of liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 in mice was significantly reduced, the contents of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and blood glucose concentration were decreased, and the mRNA expressions of TNF-a, IL-6 and interference – γ were decreased. Further studies have shown that honokiol can increase the expression of SOD, catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSH PX) and glutathione reductase (GR), and protect the liver by enhancing the antioxidant capacity of liver tissue.
Effects on metabolism
Hypoglycemia
Chen et al. Reported that magnolol can increase serum creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and other cardiac serological indexes in type I diabetic mice induced by hyperglycemia, improve histopathological damage, and alleviate myocardial inflammation induced by diabetes.
Sun Changhao et al. Used high-fat combined with small trick of streptozotocin to induce type 2 diabetic rats. After administration of magnolol (140mg / kg) by gavage for 4 weeks, the fasting blood glucose of rats decreased significantly, the insulin level increased significantly, and the morphological changes of islets improved, which delayed the development of type 2 diabetes. Wang Jun and other researchers found that magnolol can up regulate the mRNA expression levels of liver transporters OAT2 and OATP2B1, and down regulate the mRNA expression levels of renal transporters BCRP and MRP4, so as to achieve the effect of anti diabetes. In addition, sun et al. Gavaged dB / db diabetic mice with Magnolia officinalis ethyl acetate extract (0.5g/kg) for 4 weeks, the fasting blood glucose level was significantly decreased. Further study found that honokiol also had the effect of reducing blood glucose in type 2 diabetic mice, and it may be through inhibiting the activity of protein tyrosine phosphate 1b enzyme and activating insulin signaling pathway. Honokiol can also significantly increase the accumulation of lipid in the process of preadipocyte differentiation. When treated with ppapy antagonist GW9662, the effect of honokiol on 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation into mature adipocytes is significantly weakened, which provides a new target for the treatment of diabetes.
Lipid lowering
Jiena et al. Found that honokiol regulated the transcription activity of liver X receptor α (LXR α) in a dose-dependent manner, and increased the protein expression of ABCA1 and ABCC1 downstream of LXR α in THP1 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner to achieve lipid-lowering effect.
Anti tumor
Yang et al. Found that honokiol can down regulate the expression of β – Catenin, c-myc, survivin, BCL XL and vimentin in a concentration dependent manner to inhibit the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cell SW1990, and inhibit its migration and invasion by down regulating the expression of β – Catenin, a key protein in Wnt / β – catenin signaling pathway. However, Wang Liwen and other researchers found that honokiol could enhance the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. In addition, magnolol and honokiol have good inhibitory effects on lung cancer cells, nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, bladder cancer cells, leukemia cells and gallbladder cancer cells in vitro.
Antioxidant
Fan et al. Studied the scavenging effects of water extract, 60% ethanol extract, 80% ethanol extract, crude polysaccharide, total alkaloids, lignans, honokiol and honokiol on superoxide anion (O2) free radical, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl free radical and three kinds of free radical 80% ethanol extract, total alkaloids, and magnolol. Li Qinghua et al. Found that compared with supercritical fluid extraction, ethyl acetate extract had the strongest antioxidant activity. Li Jiayin found that magnolol and honokiol could inhibit H2O2 induced phosphorylation of proteins in LO2 cells in a concentration dependent manner, and inhibit the phosphorylation of p38, JNK1 / 2 and ERK1 / 2 in LO2 cells in a time and concentration dependent manner, and resist H2O2 induced oxidative stress in LO2 cells through MAPKs / NF KB signal transduction pathway.
Antiinflammatory
Zhang Changmeng found that the expression levels of klf-4, NF KB, p65 and 1l-6 increased at first and then decreased after intravenous injection and magnolol injection (the peak appeared at 12 h), Therefore, honokiol can significantly down regulate the expression of transcription factor klf-4 after spinal cord injury in rats, and then down regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory genes to reduce the inflammatory response. Zhong Qibing and other researchers found that honokiol can reduce the epidermal thickness induced by imiquimod, reduce inflammatory infiltration and micro abscess, and improve the changes of psoriasis like lesions by down regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. In vitro studies have reported that honokiol can also inhibit the activation of microglia induced by mitochondrial soluble protein through the above pathway, so as to reduce the damage of nervous system caused by inflammatory reaction.
In addition, Huang Yun and other studies found that honokiol can inhibit tetrodotoxin sensitive sodium current in DRG cells in a concentration dependent manner, and reduce the excitability of DRG cells, so as to achieve the effect of treating inflammatory pain.
Antibacterial
The results showed that the extracts of Magnolia officinalis with different polarity showed certain antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and Salmonella It was found that magnolol and honokiol, the main active components of Magnolia officinalis, have broad-spectrum antibacterial activities. They can inhibit Candida albicans, Galanz positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria, and most of them are related to affecting the permeability of bacterial cell membrane. The mic and MBC of honokiol were 16 μ g / ml and 32 μ g / ml, respectively, while the MBC of mengmeizhu was 64 μ g / ml. Xiang Xiaobo and other researchers found that the inhibition rate of honokiol 123mg / L on Candida albicans reached 66.32%. In the inhibitory effect of honokiol on Staphylococcus aureus, Qiao Ruihong and other researchers found that its mic and MBC were 10 μ g / ml and 20 μ g / ml, respectively. Li Wenli found that its MICs range was 32-128 μ g / ml, and MBCs range was greater than 512 μ g / ml. Liu Dan and other researchers found that high concentration (0.75g / L) and magnolol have inhibitory effect on Helicobacter pylori, and can effectively inhibit the formation and secretion of vacuolating toxin a when it is far lower than the minimum inhibitory concentration (0.33g / L); Li Ting found that magnolol can significantly reduce the growth activity of Streptococcus mutans biofilm, reduce the proportion of viable bacteria in the biofilm, and inhibit its cariogenic virulence factor FF h. The transcription and expression of gtfd, PDP and other gene fragments lead to the destruction of biofilm structure.More Scientific research and development for Magnolia Bark Extract Powder, please check here




















