Ganoderma Lucidum Extract Attenuate Lipid Metabolism And Modulate Gut Microbiota
Although everyone knows that high-fat diet is the driving force behind hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, fatty liver, obesity and metabolic syndrome, it is still difficult to pay close attention to our mouth. It is human nature to like delicious food. Since nature is hard to resist, eat Ganoderma lucidum more.
According to the report of Journal of Functional Food published in July 2018 by Fungus and Grass Engineering Research Center of Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University, feeding rats with high-fat diet with Ganoderma lucidum extract GL55 extracted with 55% alcohol can regulate the composition of intestinal flora, gene expression and protein expression in liver, and the abnormal blood lipid and liver fat heap caused by compound high-fat diet product.

Ganoderma Lucidum Extract Attenuate Lipid Metabolism And Modulate Gut Microbiota
Rich Triterpene from Ganoderma lucidum extract by ethanol
The team used UPLC-QTOF MS-MS to analyze of Ganoderic lucidum extracted (GL55) by ethanol with 55% ethanol and found that it contained at least 15 major triterpenoids, such as ganoderic acid Me, ganoderic acid C6, ganoderic acid H and ganoderic acid D.
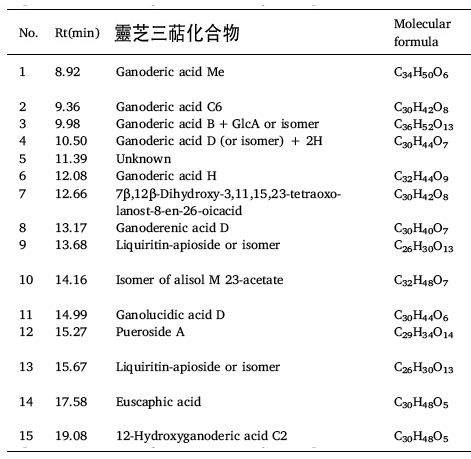
ganoderma lucidum extract by ethahol
The triterpene-rich Ganoderma lucidum extract by ethanol GL55 (150 mg/KG daily) was fed to rats with high-fat diet, and compared with rats fed with general diet, high-fat diet, high-fat diet and anti-hepatitis drug silymarin (150 mg/KG daily). Eight rats in each group were found after eight weeks:
Result 1: Improve the abnormality of blood lipid, blood sugar and liver index.
Compared with the general diet group, the serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), free fatty acid (FAA), and fasting blood sugar (FBG) related to diabetes in the high-fat diet group increased significantly, while the level of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C, commonly known as good cholesterol) decreased significantly.
In contrast, silymarin supplementation significantly reduced serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL-C, fasting blood glucose and liver function-related ALT (alanine aminotransferase, GPT) in rats fed a high-fat diet.
Surprisingly, GL55, an ethanol extract from Ganoderma lucidum, has more excellent regulatory effects than silymarin on serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL-C, fasting blood sugar, ALT and even free fatty acids in rats fed a high-fat diet.
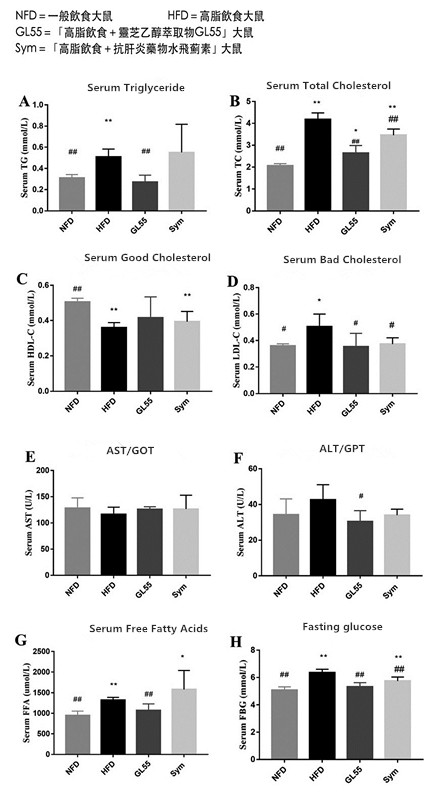
Blood test results of each group of rats
Result 2: Ganoderma lucidum reduces liver fat accumulation
In this study, normal lobular and cellular structures were observed in liver tissue sections of the general diet group (Fig. 2A). In contrast, the gap between hepatocytes in the high-fat diet group became larger and looser, and many cells were found to rupture, autolysis and necrosis (Fig. 2B).
Compared with high-fat diet group, silymarin-supplemented high-fat diet group significantly reduced the amount of fat accumulated in the liver (Fig. 2C); Ganoderma lucidum ethanol extract GL55 group showed similar morphology to the former, but a small amount of fat droplets could be observed (Fig. 2D). Obviously, triterpene-rich Ganoderma lucidum extract ethanol GL55 can prevent fatty liver formation to extent.
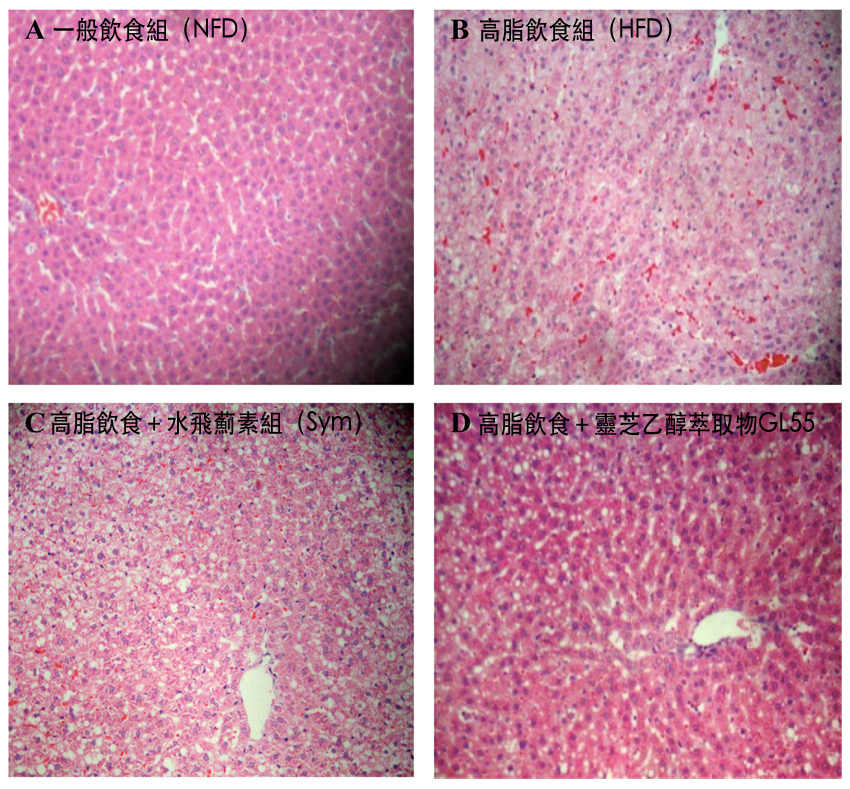
Fig 2 sections for liver tissue of different rats group
Result 3: Regulation of intestinal microflora composition
According to recent studies, intestinal microflora not only affects the energy metabolism of the host, but also affects the changes of various lipid contents in the serum of the host. Therefore, researchers randomly selected five rats from each experimental group and analyzed their cecum microflora (the initial segment of large intestine, the junction of small intestine) by principal component analysis (PCA).
The results of PCA analysis in Fig. 3 show that although there are great individual differences, the trend shows that high-fat diet can change the structure of cecum microflora in rats compared with general diet, but the extract of Ganoderma lucidum GL55 has a partial reversal effect. The supplementation of this extract can make the cecum microflora composition of rats fed with high-fat diet closer to that of normal rats.
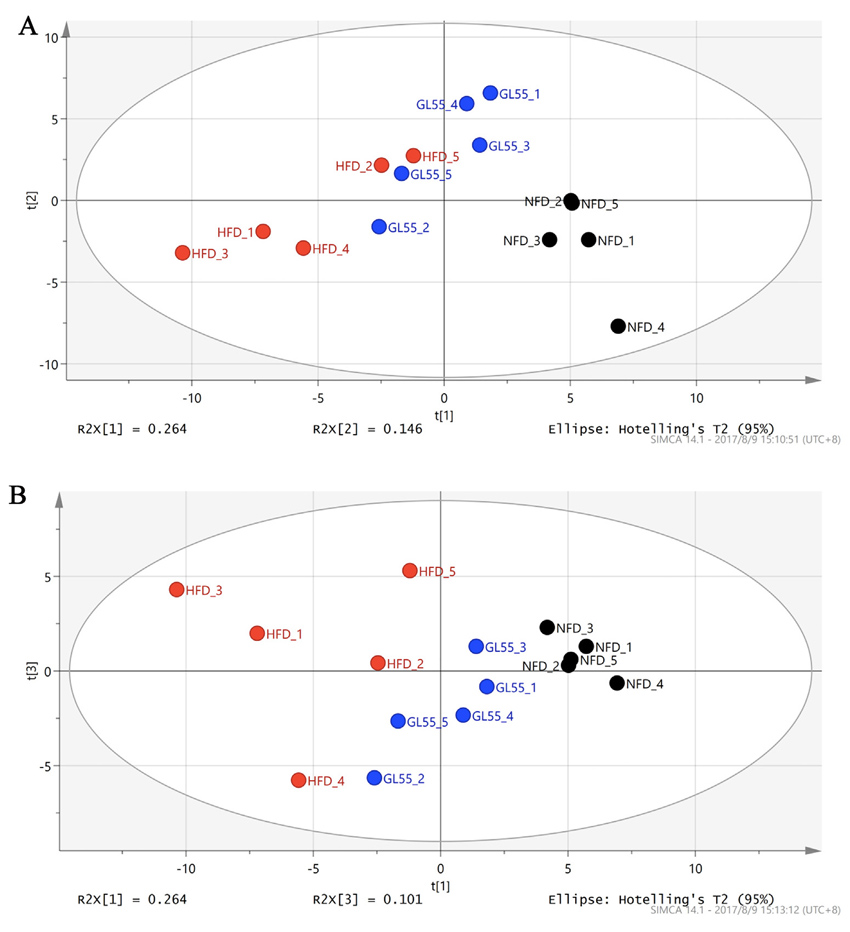
Fig 3 The composition of microflora of caecum in rats
The researchers further analyzed the types of intestinal microflora in rats. The results showed that supplementation of Ganoderma lucidum extract GL55 could significantly increase the expression of specific microflora, such as Alloprevotella, Ruminococcus, Prevotella, and reduce the proportion of Turicibacter and Lostridium XVIII in the whole microflora. These changes were basically related to hyperlipidemia, fatty liver and lipid generation. There was a negative correlation between metabolic disorder and hyperglycemia.
Result 4: Ganoderma lucidum rich in triterpenoids regulates gene and protein expression in liver
In addition, GL55 can also regulate lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in rats fed with high-fat diet by regulating gene expression (fig. 4) and protein expression (fig. 5). These changes are also beneficial to the reduction of blood lipid and blood sugar in Ganoderma lucidum and the formation of fatty liver.
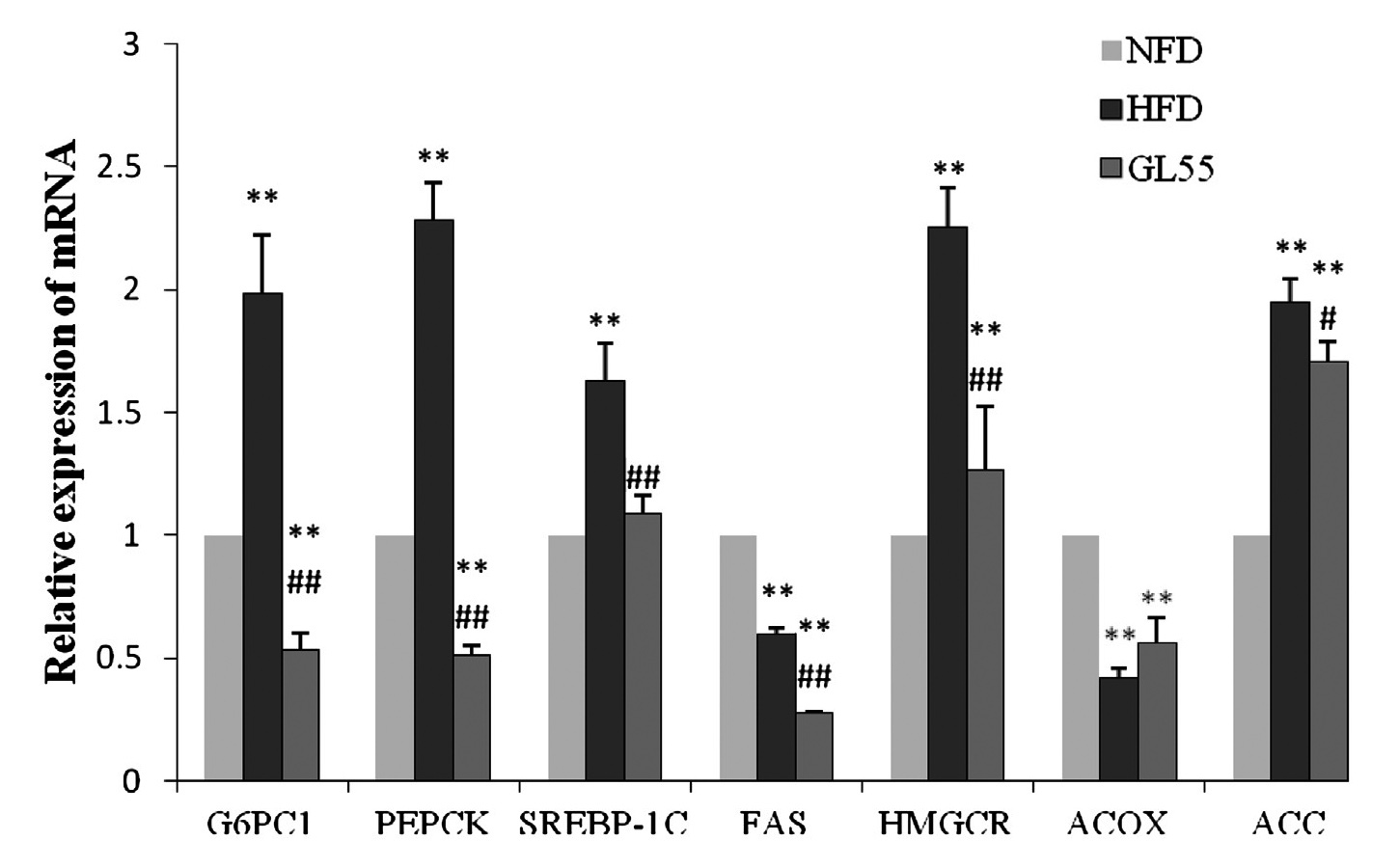
Fig 4 Analysis of gene expression in rat liver
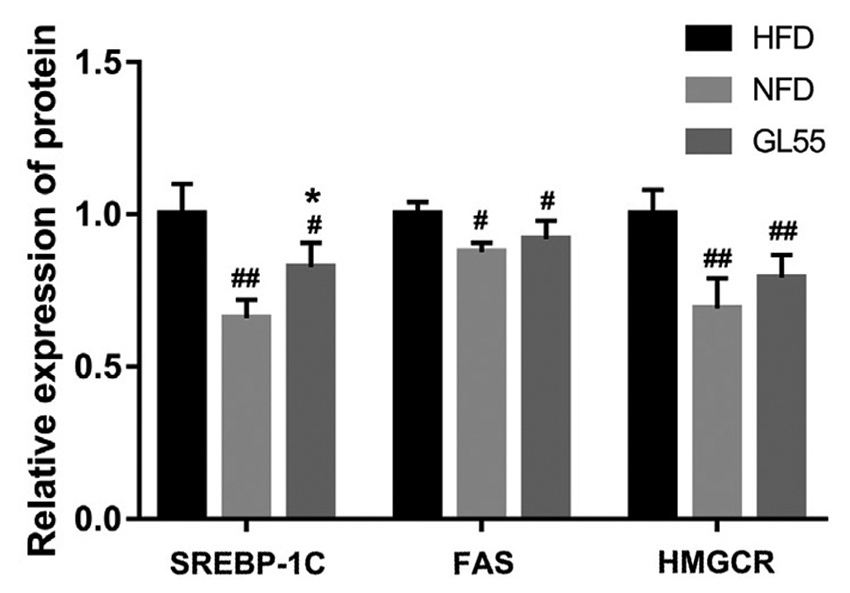
Fig 5 Analysis of hepatic protein expression in rats
In conclusion, triterpene-rich Ganoderma lucidum extract GL55-free can reverse lipid metabolism disorder induced by high-fat diet by regulating intestinal microflora, regulating liver gene and protein expression, delaying or preventing the occurrence of dyslipidemia and fatty liver.
These effects are undoubtedly the strong backing for modern people who accidentally fall into the crisis of high-fat diet, because whether it is obesity, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, the cause of metabolic disease syndrome, the spearhead is directed at lipid metabolism disorders.
Although many research teams have made great progress in the development of lipid-lowering drugs, these drugs also have many side effects and are very expensive. Fortunately, recent studies have shown that dietary regulation can regulate metabolism, and it is expected to become a more economical and safe way to treat metabolic syndrome diseases. Ganoderma lucidum extract rich in a variety of triterpenes is one of them.
Reference: RongkangHu,et al. Ganoderma Lucidum Extract Attenuate Lipid Metabolism And Modulate Gut Microbiota J Funct Foods, 2018 July;46;403-412







