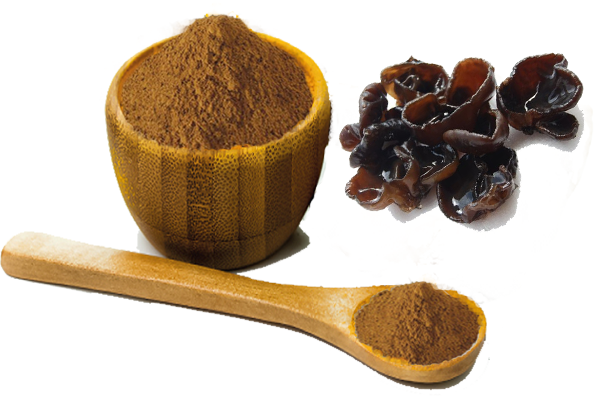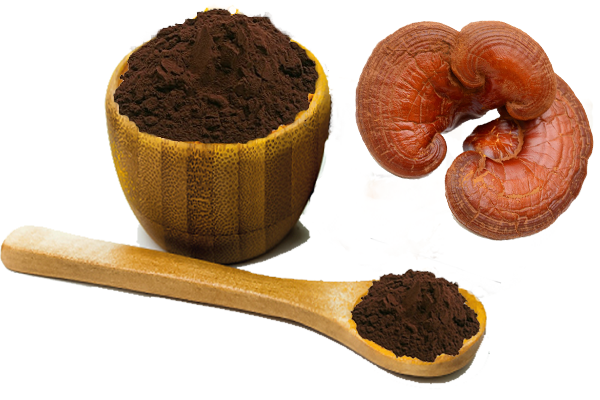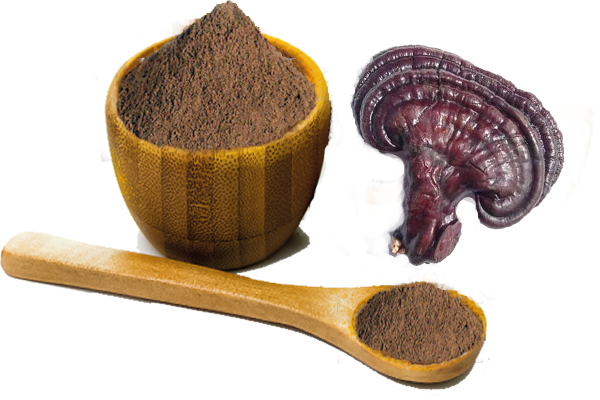
Auricularia Auricula Extract
Auricularia Auricula Extract
MIGU supplied Auricularia Auricula Extract polysaccharide 10%,20%,30%,40%,50%; refined powder and OEM service with analysis meets the EP, USP, JP, CP.....
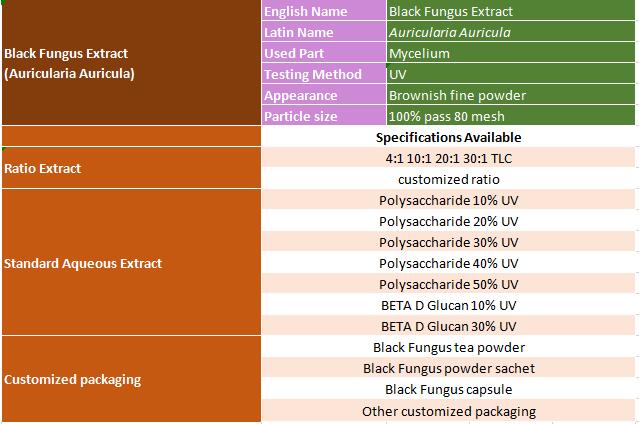
Auricularia Auricula Extract Specification
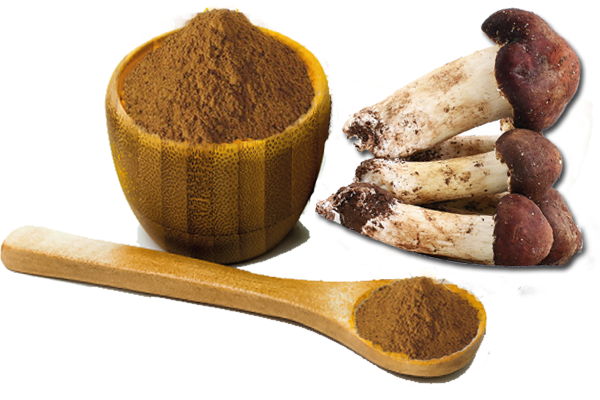
History of Auricularia Auricula Extract ( Black Fungus ) History
Black fungus, or Auricularia polytricha, is sometimes known as wood ear, cloud ear, Judas ear or tree ear. It is a mushroom that is dark brown to black and native to Asia and some Pacific islands with humid climates, according to the Mycological Society of San Francisco. It is edible and often used in Asian cooking. The mushroom can be found throughout the year in temperate regions worldwide, where it grows upon both dead and living wood. The popularity of this mushroom dates back centuries especially in China were it is extremely popular .
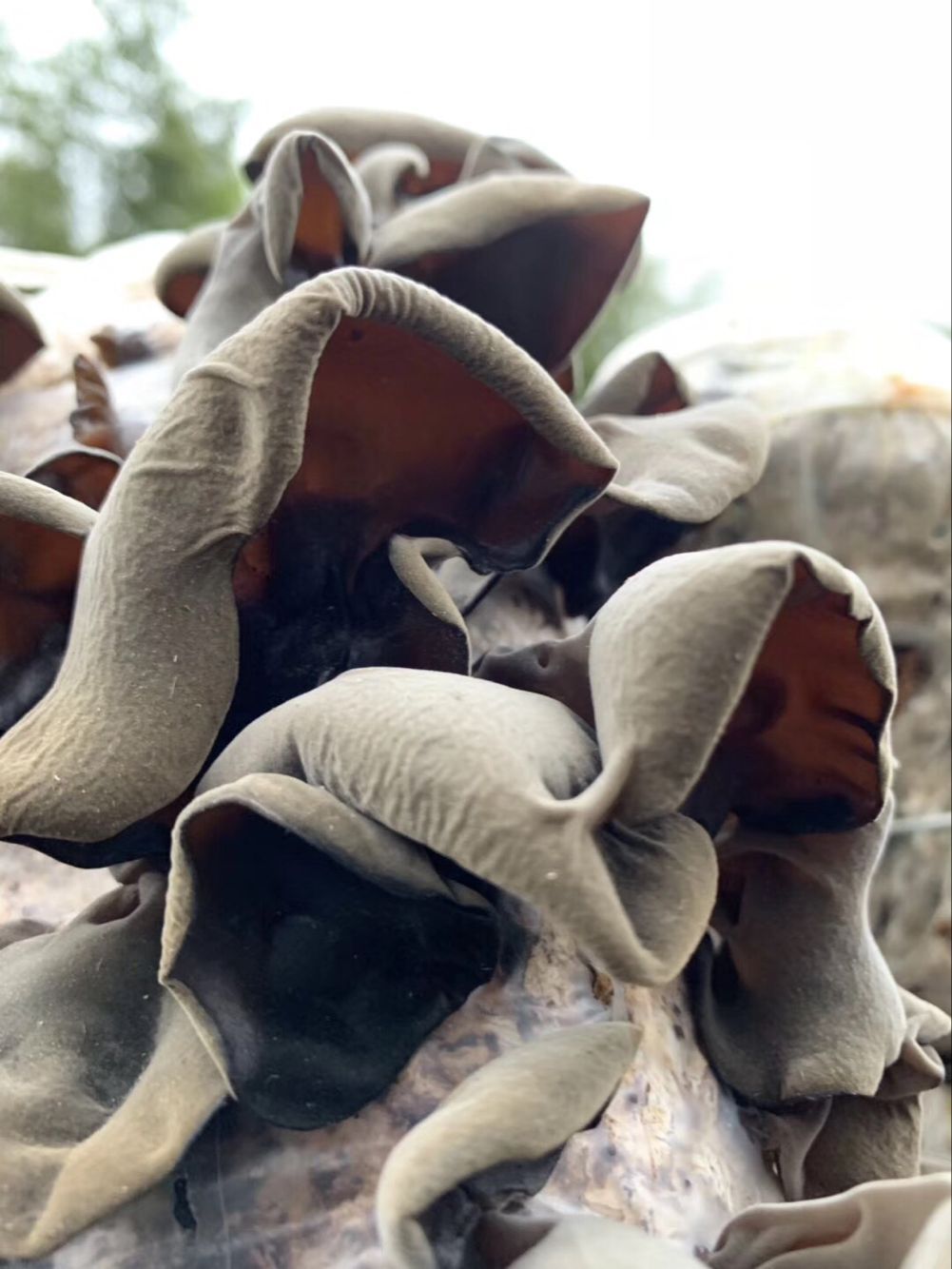

Auricularia Auricula Extract
Specifications of Auricularia Auricula Extract (Black Fungus )
Black fungus is a very common type of edible mushroom which is found in Nigeria and other parts of the world. It grows on trees mostly in the rural areas due to the vast untapped vegetation found there.It has lots of medicinal benefits due to the nutrients it contains such as Vitamins, Protein, Fat, Iron, polysaccharides and a whole lot more.
Its applications in traditional medicine include preventing iron deficiency anemia, haematemesis, uterine bleeding, hemorrhoid, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, and even cancer prevention . For more extract purity information,please see above
Origin of Auricularia Auricula Extract (Black Fungus ) — Wild and Cultivated
According to records from China this mushroom was cultivated around 600AD, making it the first recorded mushroom under cultivation. They still grow wild, China yields around 80% of the world market in production,but we supported “forest farming” method to produce Auricularia Auricula mushrooms on hardwood logs–“Grow-at-home”
Cultivation of this species is easy! Simply grow this like shiitake on hardwood sawdust blocks, but fruit it at a warmer temperature of 25°-30°C. Fruit bodies are slightly larger than A. auricula-judae and measure 6-20cm across.
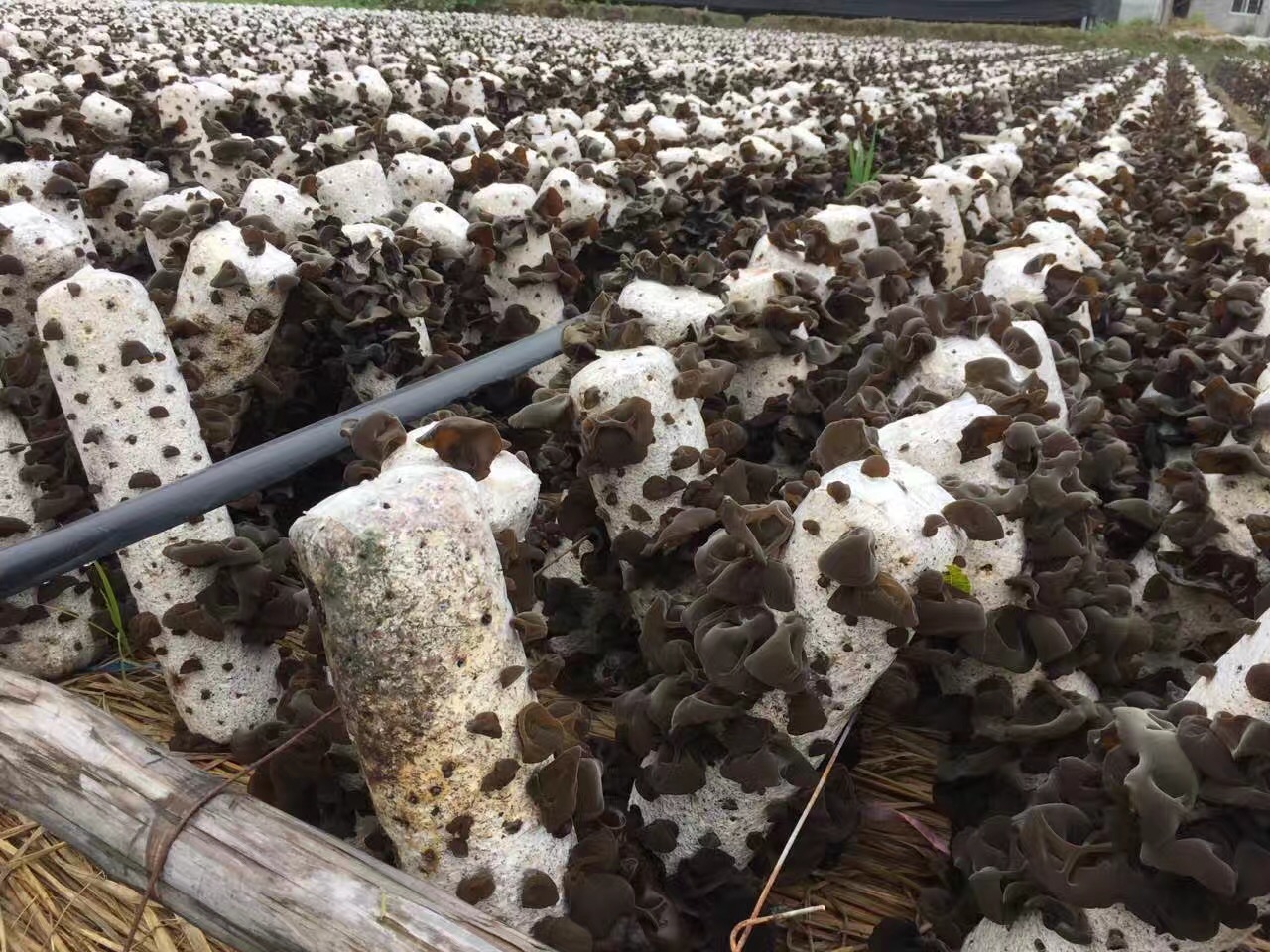

Auricularia Auricula Extract Planting Base
Most popular species under cultivation are naturally wood inhabiting fungi. So, growing on sawdust is a logical choice. Sawdust is mixed with wheat bran (or another nitrogen source) at 5-15% and Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) (a buffering agent) at 2-3%, and filled into autoclavable bags. The bags are sterilized for a minimum of 1 hour at 121°C (15 psi when at sea level). Note sterilization exposure times vary depending on pressure and elevation. Finally, the substrate is cooled to at least 25°C (approx. 80°F) then, inoculated with grain or liquid spawn and incubated at appropriate temp for the species until colonization is complete.
Auricularia Polytricha has high medicinal value, it has ziyin strong, clear lung qi and invigorate the circulation of blood and hemostasis analgesic function, such as textile and mine workers in good health food products, and according to the reported. Auricularia Polytricha polysaccharide on the back of the villi contains abundant hair, is one of the strongest six in antitumor activity (other ganoderma lucidum, versicolor, birch plait hole bacteria, the tree, red tongue bacteria).
Pharmacology of Auricularia Auricula Extract ( Black Fungus )
Auricularia auricula-judae has been the subject of research into possible medicinal applications. Experiments in the 1980s concluded that two glucans isolated from the species showed potent antitumour properties when used on mice artificially implanted with Sarcoma 180 tumours. This was despite the conclusion of earlier research indicating that, while aqueous extracts from several other fungal species had antitumour effects, extracts from A. auricula-judae did not.
Further, research on genetically diabetic mice showed that a polysaccharide extracted from A. auricula-judae had a hypoglycemic effect; mice fed with food including the polysaccharide showed reduced plasma glucose, insulin, urinary glucose and food intake.
Another chemical extracted from the species was an acidic polysaccharide (made up of mostly mannose, glucose, glucuronic acid and xylose) which showed anticoagulantproperties. The article concluded that “the polysaccharides from these mushrooms may constitute a new source of compounds with action on coagulation, platelet aggregation and, perhaps, on thrombosis”.
Benefits of Auricularia Auricula Extract ( Black Fungus )
It has been a part of traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. The range of ailments specified for treatment is so broad and varied it is difficult to conceive of how the fungus could be effective for so many unrelated maladies.
Like many mushrooms, Auricularia species contain polysaccharides, some of which are known to be immunostimulatory and inhibitory toward cancer cells. Antiviral, antibacterial and cholesterol lowering effects have also been described, but these are general properties of fungal polysaccharides and there has been little work on these potential activities with respect to Auricularia. Some reputable research has indicated anticancer potential as well as anticoagulant and hypoglycemic effects.
One report notes that drinking tea made from wood ear fungus was popular for a time in Britain, but the extreme acidity of the concoction caused stomach troubles so the practice has been discontinued.
A: Improves Circulation
The Mycological Society of San Francisco states that black fungus has a chemical that inhibits blood clotting, and because heart attacks, strokes and blood vessel diseases are linked to clotting, this fungus may improve circulation. Veg for Life also states that it contains anticoagulant substances that act like blood thinners, similar to that of aspirin.
B : Lowers Cholesterol
Black fungus may lower cholesterol and blood sugar, according to the Sierra Club Pro website. Laboratory testing in mice found that this type of fungus had a hypoglycemic effect on obese mice. Serum LDL cholesterol levels were reduced by 24 percent in the mice tested.
C: Hemorrhoids
Due to the ability of black fungus to help with blood circulation, it is also useful in helping with hemorrhoids, according to Chinese Medicine Gem. It has a cooling effect on the blood, promoting circulation and treating bruises, which may be why it is used to treat hemorrhoids.
D: Lowers Cholesterol
Black fungus may lower cholesterol and blood sugar, according to the Sierra Club Pro website. Laboratory testing in mice found that this type of fungus had a hypoglycemic effect on obese mice. Serum LDL cholesterol levels were reduced by 24 percent in the mice tested
E: Dryness
Black fungus is beneficial to people suffering from dryness, such as a dry throat, cough or mouth, according to the Institute of Chinese Medicine. It is thought to moisten the blood and promote circulation, which alleviates conditions associated with dryness.
F: Anti-viral
According to Veg For Life, black fungus contains the trace mineral germanium, which has anti-viral and anti-tumor effects. Germanium is also known to energize the body, which is why it is useful as an herb that fights off viruses.
Other Benefits for Auricularia Auricula Extract
In Chinese medicine, herbs such as black fungus are used to promote positive emotions and help with feelings of isolation, fear and insecurity, according to a Pacific College of Oriental Medicine article. Black fungus is thought to help people resist hunger, help with uterine bleeding, gonorrhea and intestinal issues, according to Chinese Medicine Gem.
More Organic Fungus Extract from MIGU: reishi, cordyceps, chaga, shiitake, maitake, agaricus blazai, agaricus bisporus
Reference
1.Apetorgbor et al. 2005, p. 10
2.Misaki, A.; Kakuta, M.; Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, M.; Miyaji, H. (1981). “Studies on interrelation of structure and antitumor effects of polysaccharides: antitumor action of periodate-modified, branched (1→3)-β-D-glucan of Auricularia auricula-judae, and other polysaccharides containing (1→3)-glycosidic linkages”. Carbohydrate Research 92 (1): 115–29.doi:10.1016/S0008-6215(00)85986-8. PMID 7196285.
3.Ikekawa, Tetsuro; Uehara, Nobuaki; Maeda, Yuko; Nakanishi, Miyako; Fukuoka, Fumiko (1968). “Antitumor activity of aqueous extracts of ediblemushrooms”.Cancer Research 29 (3): 734–5. PMID 5813100.
4.Yuan, Zuomin; He, Puming; Cui, Jianhui; Takeuchi, Hisanao (1998). “Hypoglycemic effect of water-soluble polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula-judae Quel. on genetically diabetic KK-Ay mice”. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 62 (10): 1898–1903.doi:10.1271/bbb.62.1898. PMID 9836425.
5.Yoona, Seon-Joo; Yub, Myeong-Ae; Pyunb, Yu-Ryang; Hwangb, Jae-Kwan; Chuc, Djong-Chi; Juneja, Lekh Rajc; Mourão, Paulo A. S. (2003). “The nontoxic mushroomAuricularia auricula contains a polysaccharide with anticoagulant activity mediated by antithrombin”.Thrombosis Research 112 (3): 151–8.doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2003.10.022. PMID 14967412.
6.Francia, Christelle; Rapior, Sylvie; Courtecuisse, Régis; Siroux, Yves (1999). “Current research findings on the effects of selected mushrooms on cardiovascular diseases” (PDF). International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms 1: 169–72.
7.Marlowe, Christopher (1633). The Jew of Malta.
8.8.Harding 2008, pp. 193–4


















