Evaluation of Immune Modulation by beta glucan ganoderma lucidum extract in Healthy Adult Volunteers, A Randomized Controlled Trial
Researchers from the College of Life Science at National Taiwan University, the College of Life Science at National Taiwan Ocean University, and Taipei Hospital of the Ministry of Health and Welfare jointly published a clinical trial result in the February 2023 issue of *Food* (a food science journal), demonstrating that daily consumption of *Ganoderma lucidum*-derived beta-glucan (referred to as “salt-zhī beta-glucan”) can indeed enhance immunity.

Evaluation of Immune Modulation by Beta-1.3;1.6 D-Glucan Derived from Ganoderma Lucidum Extract in Healthy Adult Volunteers, A Randomized Controlled Trial
The clinical trial was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the *Declaration of Helsinki* and approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB). All study records were registered with the International Standard Randomized Controlled Trial Number (ISRCTN) registry (ID: ISRCTN48306294).
The trial adopted a randomized, double-blind (neither participants nor researchers knew group assignments), placebo-controlled design. It evaluated the effects of daily intake of *Ganoderma lucidum* beta-glucan over 12 weeks (84 days) on immunity, safety, and tolerance in healthy individuals aged 18–55, based on changes in blood biochemical parameters before and after the intervention.
The beta-glucan supplement provided to participants was a capsule formulation primarily composed of beta-glucan extracted from *Ganoderma lucidum* mycelium, constituting approximately 75.2% of the capsule. At a daily dose of one 200 mg capsule, participants consumed about 150.4 mg of *Ganoderma lucidum* beta-glucan, along with non-beta-glucan carbohydrates (15.8%), fats (1%), proteins (1%), ash (2%), and moisture (5%).
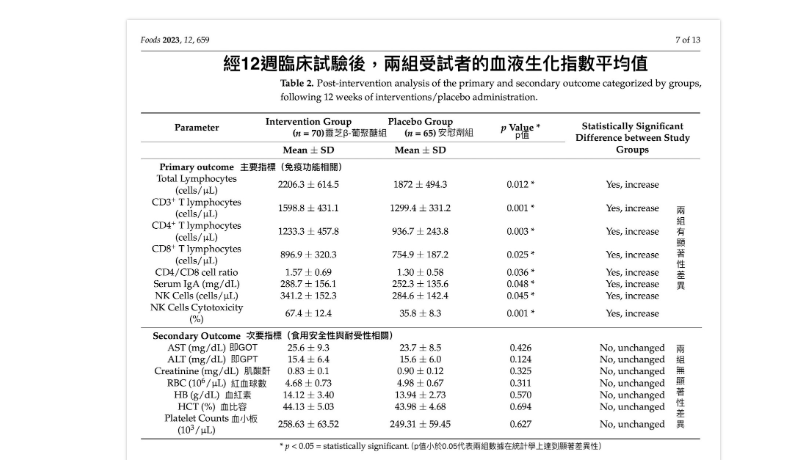
After nearly three months of intervention, what immunological changes were observed in the 70 healthy participants? Results showed significant increases in total lymphocyte counts (including T cells, B cells, and natural killer [NK] cells), total T cells (CD3+), T cell subsets (CD4+ helper/regulatory T cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells), the CD4/CD8 ratio, NK cell counts and cytotoxic activity, and IgA antibody concentrations—all within ranges considered beneficial for combating infections and maintaining health. These changes were not observed in the placebo group (65 participants).
Additionally, researchers analyzed the safety of long-term beta-glucan consumption by monitoring liver function indices, renal function indices, red blood cells, platelets, and other blood biochemical markers. No statistically significant differences were found between the two groups before and after the trial, indicating that *Ganoderma lucidum* beta-glucan safely modulates immune function in healthy adults without adverse effects and exhibits good tolerability.
Evaluation of Immune Modulation by Beta-1.3;1.6 D-Glucan Derived from Ganoderma Lucidum Extract in Healthy Adult Volunteers, A Randomized Controlled Trial 2
For a long time, the purported immune-boosting effects of *Ganoderma* (lingzhi/Reishi mushroom) supplements in humans have largely relied on subjective personal experiences or anecdotal reports (e.g., fewer colds). Even the few existing clinical studies either focused on immunocompromised populations (e.g., cancer patients, the elderly) or suffered from flawed designs (e.g., lack of placebo control groups) or informality (e.g., no ethical review board approval). Now, the emergence of this clinical trial report reinforces the rationale for daily *Ganoderma* supplementation.
Natural killer (NK) cells are key players in innate immunity, capable of rapidly attacking pathogens and cancer cells. T cells act as commanders of adaptive immunity, tailoring immune responses to specific pathogens or cancer cells based on frontline intelligence. IgA antibodies circulate in the bloodstream, neutralizing previously encountered pathogens to prevent infections.
Thus, daily supplementation with *Ganoderma* beta-glucan, which enhances these immune markers, clearly supports improved defenses against infections and tumors (at least in healthy adults)—without harming liver or kidney function or disrupting hematopoiesis.
[Note 1] While the full report does not mention “fruiting bodies” and emphasizes that the raw material (used to produce beta-glucan) originated from the U.S. and was confirmed as *Ganoderma lucidum* by BCRC (Bioresource Collection and Research Center), further online research based on contextual clues confirms that the beta-glucan in this trial was derived from mycelium.
[Note 2] Beta-glucan is a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules linked by specific bonds (e.g., β-1,3 backbone with β-1,6 and/or β-1,4 branches). It is a key component of fungal and plant cell walls. Studies suggest that *Ganoderma*-derived beta-glucan resists degradation by gastrointestinal enzymes due to its unique structure, enabling it to modulate gut microbiota and activate intestinal immune cells.
Reference: Shiu-Nan Chen, et al. Evaluation of Immune Modulation by Beta-1.3;1.6 D-Glucan Derived from Ganoderma Lucidum Extract in Healthy Adult Volunteers, A Randomized Controlled Trial. Foods. 2023 Feb 3;12(3):659. doi:10.3390/foods12030659







